Internetfähige Geräte sind längst unverzichtbar im Alltag. Wi-Fi nehmen wir als selbstverständlich hin – bis es stockt oder ausfällt. Zu Hause oder unterwegs fühlt man sich ohne stabile Verbindung verloren. Langsame Downloads oder Streaming können den Tag versauen.

Als WLAN-Experten kennen wir die besten Lösungen gegen schwache Signale. In diesem praxisnahen Guide zeigen wir Ihnen bewährte Methoden, um WLAN- und Mobilfunkgeschwindigkeiten zu maximieren. Lernen Sie, Datennutzung zu senken, Einstellungen zu optimieren, Nachbarn fernzuhalten und Probleme zu beheben – durch Hardware-Upgrades, smarte Apps oder einfache Anpassungen. Los geht's!
Schnelleres WLAN zu Hause erzielen
Es gibt vielfältige Wege zu mehr Geschwindigkeit: vom mobilen Hotspot bis zum Bandwechsel. Hier die effektivsten Strategien für Ihre Internetverbindung.
Option 1: Mesh-WLAN-System einrichten
In großen Häusern mit dicken Wänden entstehen oft tote Zonen. Ein Range-Extender hilft, aber ein Mesh-System ist die Top-Lösung. Es verteilt starkes, stabiles WLAN flächendeckend über mehrere Zugangspunkte, die nahtlos zusammenarbeiten. Starten Sie mit einem Router am Modem und erweitern Sie bei Bedarf.
Dieses System ist investitionsstark, liefert aber überlegene Ergebnisse. Google Nest Wi-Fi überzeugt durch einfache Einrichtung via Google Home App, integrierten Google Assistant und Lautsprecher. Preis: Router 169 USD, Punkte (Extender) 149 USD. Sparen Sie mit Packs: Router + 2 Punkte für 349 USD (Ersparnis 118 USD).
Alternativ: Linksys Velop – app-gesteuert, Alexa-kompatibel, keine separaten Router/Extender. Preise ab 129 USD bis 399 USD, günstiger in Multipacks.
Option 2: WLAN-Signal optimieren
Geschwindigkeit hängt stark vom Signal ab. Positionieren Sie den Router zentral, fern von Wänden, Geräten oder Kabeln. Für USB-WLAN-Adapter: Verwenden Sie Verlängerungskabel, um Störungen zu minimieren – das wirkt wirklich!
Wechseln Sie Adapter oder nutzen Sie einen zweiten Router als Repeater. Mesh (Option 1) bleibt jedoch unschlagbar.
Schnelleres WLAN unterwegs
Option 1: Mobiles Mi-Fi-Router nutzen
Mobile Router bieten oft Priorität bei Daten, abhängig vom Anbieter. Smartphones als Hotspot überlasten sich; Mi-Fi-Geräte handhaben mehrere Verbindungen effizient mit 3G/4G/5G.
Modelle wie Netgear Nighthawk M1 (MR1100-100NAS): Beliebige SIM, bis 20 Geräte, Dual-Band (2,4/5 GHz).

Option 2: Langsame Netze meiden
Freies WLAN ist oft langsamer als Mobilfunk. Auf Android: Einstellungen > WLAN > Drei-Punkte-Menü > "Gespeicherte Netze". Wählen Sie und "Vergessen" – keine Auto-Verbindung mehr.
Option 3: Automatischer Hotspot-Wechsel
Android 8+ unterstützt Passpoint (Hotspot 2.0) für nahtlosen Wechsel ohne Login.
Option 4: Flugzeug-WLAN optimieren
Apps aktualisieren, Hintergrund-Updates deaktivieren, Fotos-Backup stoppen. Seiten vorab laden für Caching.
Android auf 5-GHz-Band zwingen
5 GHz ist schneller und weniger überlastet. Einstellungen > WLAN > Erweitert > "WLAN-Frequenzband" > "Nur 5 GHz".
Geschwindigkeiten testen
Nutzen Sie Speedtest.net, fast.com oder OpenSignal-App – vergleicht WLAN, 3G/4G und zeigt Datennutzung.
Weitere Tipps für mehr WLAN-Geschwindigkeit
Häufige Probleme beheben
Stau, Störquellen oder Kanalüberlappung? Xirrus Wi-Fi Inspector zeigt SSID, Kanal, Signalstärke und Nachbarnetze.
Störungen lokalisieren
Wi-Fi Analyzer (Android) scannt Kanäle und Signale – wechseln Sie zum freien Kanal.
Tote Zonen finden
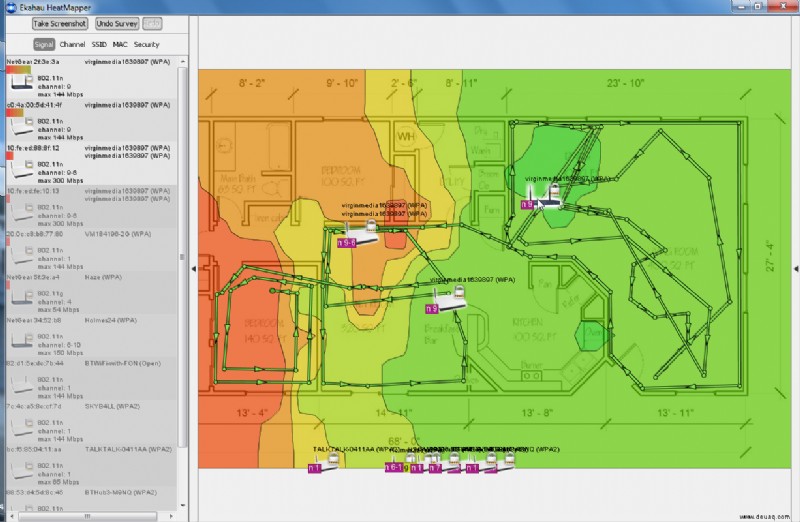
Ekahau Heatmapper erstellt Heatmaps auf Laptops/Tablets. Bewegen Sie sich, messen Sie – ideal mit Grundriss.
App-Performance prüfen
Meteor (OpenSignal) testet Download/Upload/Ping und App-Geschwindigkeiten (YouTube etc.).
Datensparmodus mit Opera
Opera Browser/Mini komprimiert Daten bis 90 %, blockt Ads, spart Bandbreite.
DataEye für Android
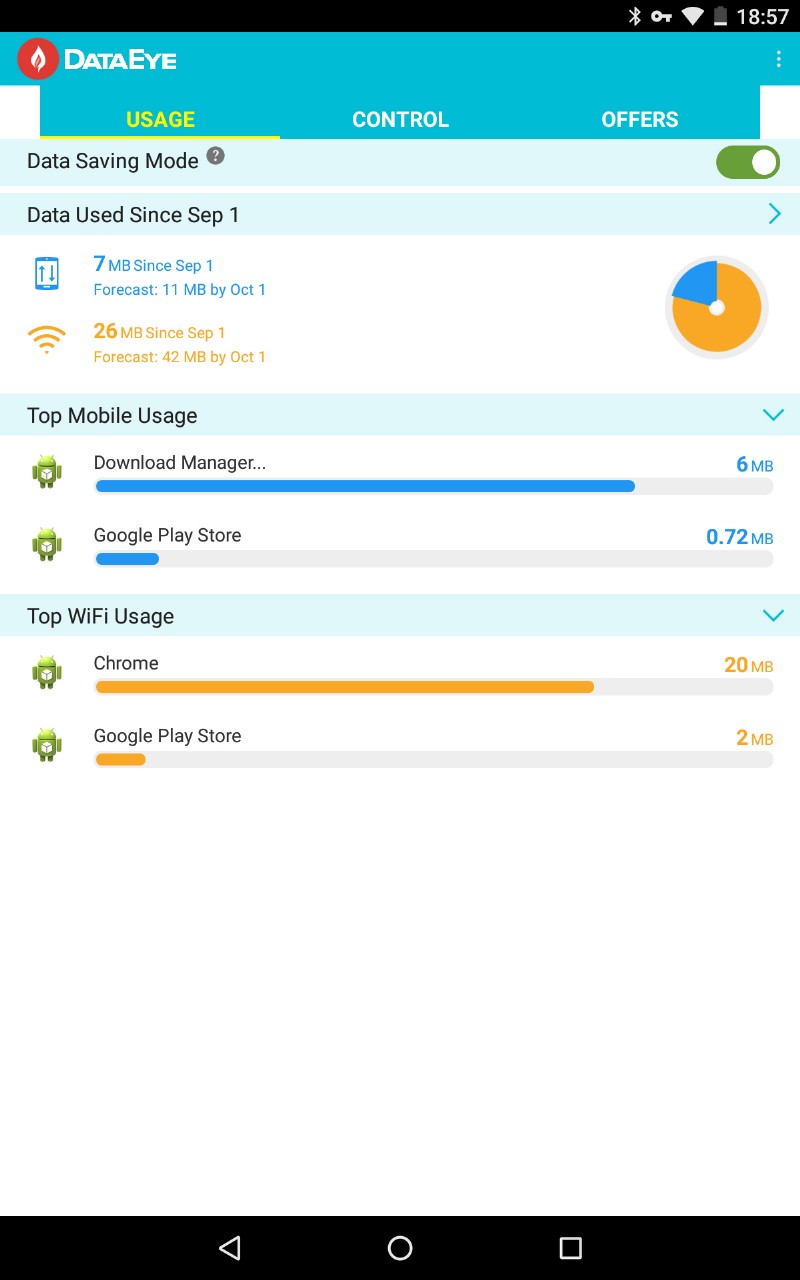
Priorisiert Apps, zeigt Verbrauch – temporäre Freigaben möglich.
Android Data Saver
Einstellungen > Netzwerk > Datennutzung > Data Saver aktivieren. Apps auf WLAN beschränken, Ausnahmen möglich.
Download-Manager
Advanced Download Manager (Android) oder Total/Offline (iOS) – multi-threaded, resumierbar.
WLAN-Diebe aufspüren und stoppen
Bitdefender Home Scanner prüft Schwachstellen und Unbekannte. Wireless Network Watcher oder Angry IP Scanner listen Geräte – scannt im Hintergrund.